Absolute Relative XPath in Selenium:
What is XPath:
- XPath is nothing but the XML path of WebElement.
- It helps to detect any element on any web page that uses the conventional XML path expression.
- XPath uses HTML DOM structure that looks like XML path expression.
Syntax for XPath:
1 | Xpath=//Tag_name[@attribute_name=’Attribute_value’] |
- // : Used to select the current node.
- Tag_name: Name of the tag of a particular node.
- @: Used to select to select attribute.
- Attribute_name: Name of the attribute of the node.
- Value: Value of the attribute.
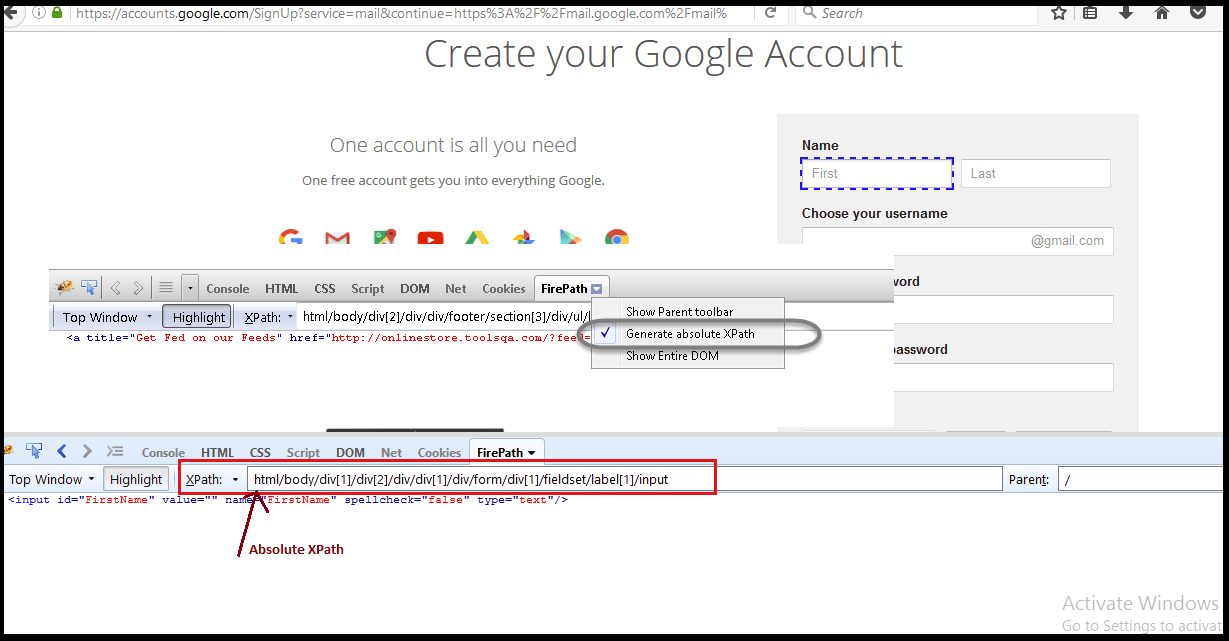
1. Absolute XPath:
- Absolute XPath starts with the root node.
- It is also called complete or full XPath.
- Absolute XPath starts from <html> tag.
- it starts from single slash(/).
Example:
1 | html/head/body/form/table/tbody/tr/th |
Choosing Absolute xpath using FirePath:
2. Relative Xpath:
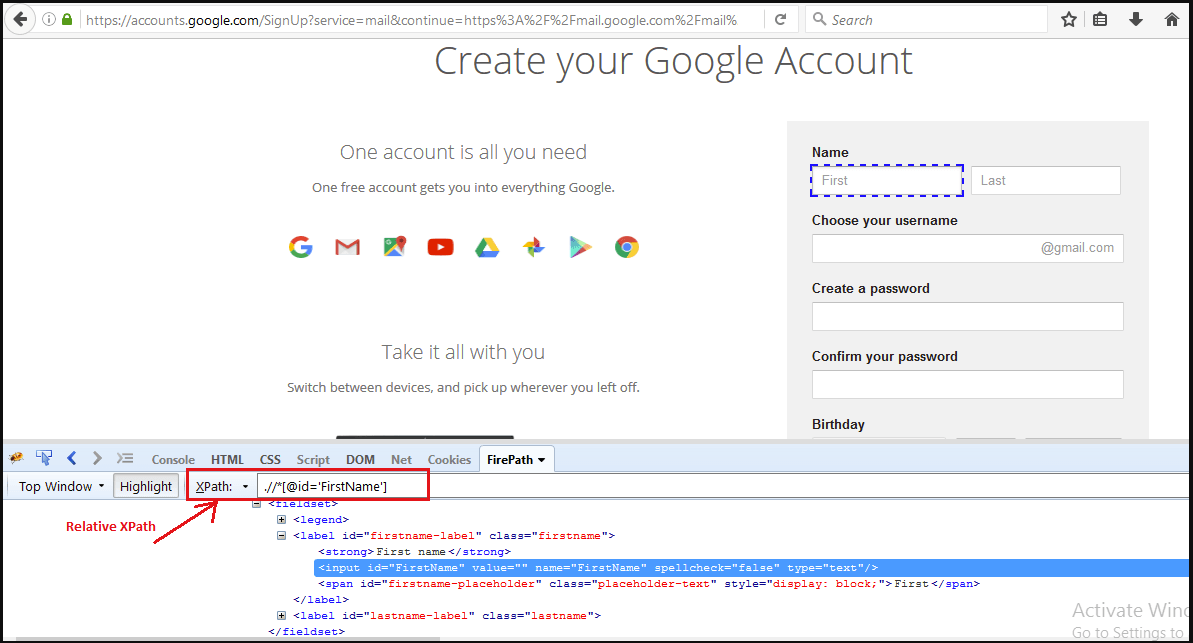
- A relative xpath is one where the path starts from the node of your choice.
- it doesn’t need to start from the root node.
- It starts with Double forward slash(//).
Example:
1 | //*[@id=’login’]/ul/li[3]/a |
Choosing Relative xpath using FirePath:
3. Difference between single ‘/’ or double ‘//’:
“/”:
- It starts selection from the document node.
- It Allows you to create ‘absolute’ path expressions.
Example: “/html/body/a” matches all the a tag elements.
“ //”:
- It starts selection matching anywhere in the document.
- It Allows you to create ‘relative’ path expressions.
Example: “//a” matches all the a tag elements.
4. Handle Complex & Dynamic elements using XPath in Selenium:
a. Basic XPath
- XPath can be select nodes or list of nodes on the basis of attributes like ID , Name, Classname, LinkText etc.
1 | Xpath=//input[@name='ele_id'] |
b. Contains()
- Contains() is used when the value of any WebElement changes dynamically, for example, login Page ID’s.
1 | Xpath=.//*[contains(@name,'ele_id')] |
c. Using OR & AND
- OR in the expression, two situations are used, whether the first condition OR the second position is correct.
- It also applies if one condition is true or may be both. This means that to find the element one condition must be correct.
- Under XPath expression, it identifies elements whose one or both conditions are true
1 | Xpath=//*[@type='submit' OR @name='Submit_Btn'] |
d. Text()
- Find the element with exact text match.1Xpath=//td[text()='ID_Name']
Example of Absolute Relative xpath in Selenium:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver; import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver; import org.openqa.selenium.support.ui.Select; import org.openqa.selenium.By; public class Xpath_Selection { public static void main(String[] args) { System.setProperty("webdriver.firefox.marionette", "C:\\geckodriver.exe"); WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver(); driver.get("https://www.stqatools.com"); // Absolute xpath driver.findElement(By.xpath("html/body/table/tbody/tr[1]/td")); // Relative xpath driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id='menuicon']")); } } |
What is the difference between absolute and relative xpaths and Different ways of choosing xpath in Selenium WebDriver
